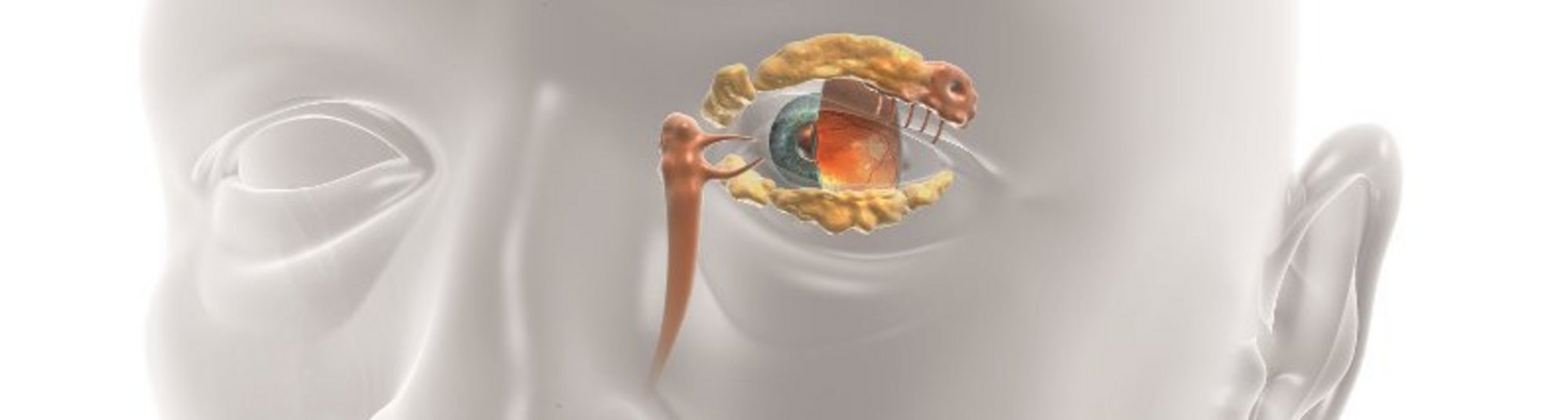
Ophthalmology - laser surgery with fiber optics
Outpatient laser surgery in private practices or clinics has become firmly established and widely accepted as a method for surgical operations over the last ten years. Operations with very little bleeding, due to the excellent coagulation of the fibercontrolled diode laser, can be effectively performed in little time and usually under local anesthetic. That is why biolitec Vista has specialized in the field of ophthalmology in the treatment with laser surgery.
Contact Wanted
With its extremely thin laser fiber, the biolitec® laser can be used safely and precisely on the sensitive structures of the eye when using the contact mode. Compared with other lasers that use the open beam mode, using the contact mode with the fibers prevents the risk of damage to surrounding tissue. Only upon contact with the target tissue will the energy of the diode laser be activated in very small pulses, with the result that all the energy of the laser is immediately absorbed at the tip of the fiber. The depth of thermal damage is therefore minimal.
NEW
The latest development of biolitec® is the "Sharp tip" fiber with a needle-shaped fiber tip specially developed for microsurgical interventions: This fiber is available in four different contact point diameters (0.25 mm, 0.20 mm, 0.15 mm and 0.10 mm) and is thus the first laser fiber in the world that can cut and coagulate without coupled or adapted separate endings. With it, surgical interventions can be carried out in the smallest possible space with unprecedented precision. Thanks to the special biolitec® diode laser, cutting and coagulation is possible at the same time in proven function at a wavelength of 1470 nm.
A laser scalpel made of a homogeneous piece of glass fiber.
Fields of application:
- Blepharoplasty (Removal of the fat deposits in the tear sac): Discission, endocoagulation and lipolysis
- Sicca syndrome (“Dry eye”): Narrowing / occlusion of the evacuative lacrimal duct (laser coagulation for punctum stenosis)
- Dacryocystorhinostomy (DCR): Opening or bypassing an obstructed lacrimal sact or nasolacrimal duct
- Watery eyes (epiphora): Opening of the evacuative lacrimal duct (Laser tip endoprobing)
- Tumor surgery (Benign fibroids, xanthelasma, xanthoma, etc.): Coagulation, vaporization and excision
- Telangiectasia (dilated capillaries): Coagulation under enlarged view
- Chalazia, Styes: Vaporization and coagulation of the inflammation / cysts in and around the meibomian glands or glands of Zeis with extensive retention of the secretory tissu
- Orbital hemangioma (“Port-wine stain”): Coagulation and vaporization